Image Authenticity Explained: Verify Photos & Provenance
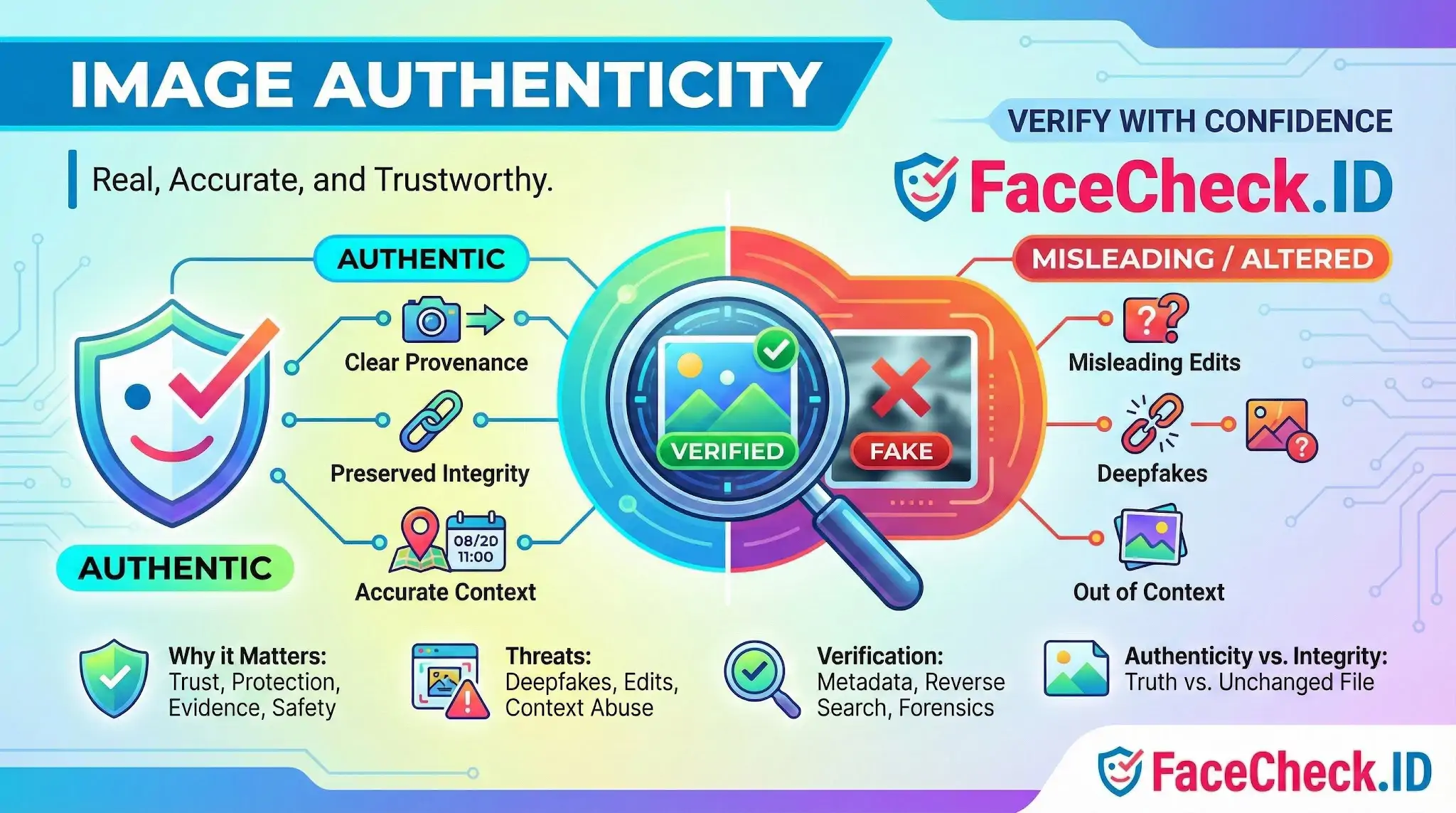
Image authenticity means an image is real, accurate, and trustworthy in what it shows. It confirms that a photo or graphic has not been altered in a misleading way and that its origin and editing history can be verified.
Image authenticity matters in journalism, ecommerce, legal evidence, marketing, social media, and AI generated content because edited or synthetic images can change meaning, mislead viewers, or damage credibility.
What makes an image authentic
An image is typically considered authentic when it meets these points:
- Provenance is clear
The creator, source, and where it came from are known or can be traced.
- Integrity is preserved
The content has not been manipulated to misrepresent reality. Minor edits like cropping or color correction can still be authentic if they do not change the meaning.
- Context is accurate
The image is presented with correct captions, dates, locations, and descriptions.
- Verification is possible
There is supporting evidence such as original files, metadata, camera details, or cryptographic records.
Common threats to image authenticity
- Misleading edits like removing objects, compositing people into scenes, or changing backgrounds
- Deepfakes and synthetic images created by generative AI tools
- Out of context reuse where a real image is paired with false claims about time, place, or event
- Metadata stripping or spoofing that hides or fakes camera and edit information
- Copy and repost chains that reduce traceability and increase the chance of misinformation
How image authenticity is verified
Professionals use a mix of technical and contextual checks:
- Metadata review to inspect EXIF and editing history when available
- Reverse image search to find earlier versions and identify the original source
- Error level analysis and forensic checks to spot inconsistencies from editing
- Source validation by contacting the photographer, publisher, or organization
- Content credentials such as C2PA based signing that records capture and edit steps
Image authenticity vs image integrity
- Image authenticity focuses on whether an image is truthful and trustworthy in its message and origin.
- Image integrity focuses on whether the file has remained unchanged from a known original, often proven with hashes or signatures.
An image can have integrity without being authentic if the original itself was staged or falsely labeled. It can also be authentic even after basic edits if the edits are transparent and non deceptive.
Why image authenticity matters
- Trust and credibility for brands, publishers, and creators
- Protection against misinformation on social platforms and news cycles
- Safer buying decisions in ecommerce where product images must match reality
- Compliance and risk reduction in regulated industries and advertising
- Evidence reliability in legal, insurance, and investigative work
FAQ
What does “Image Authenticity” mean in the context of face recognition search engines?
Image Authenticity refers to how trustworthy a face photo (the query image) or a matched result image is—i.e., whether it is a real, unmanipulated depiction of a real person at a real time/place, or whether it may be edited, composited, face-swapped, AI-generated, mislabeled, or taken out of context. In face recognition search, authenticity matters because the system can still match faces well even when the surrounding story, caption, or identity claim attached to the image is false.
Why does Image Authenticity matter when interpreting face-search matches?
Because a convincing face match does not guarantee the image’s context is true. An authentic-looking match can appear on repost sites, scam pages, or mislabeled profiles, and an inauthentic image (edited or AI-generated) can create a misleading “trail” across the web. Treat matches as leads: confirm authenticity and context before concluding the person did what a page claims or is the same person a profile claims.
What are practical checks to assess Image Authenticity after getting face recognition search results?
Common checks include: (1) open multiple results and compare dates, captions, and page purpose to see whether they agree; (2) look for the earliest credible source (original post, official site, or the highest-quality publisher) rather than repost aggregators; (3) compare multiple photos of the same claimed person for consistent features across angles/lighting (ears, moles, hairline, teeth); (4) inspect for manipulation signs (warping near edges, inconsistent shadows, blurry facial boundaries, odd reflections); (5) run both face-search and traditional reverse image search to see whether the exact image (or a crop) is circulating as a template or meme.
How do AI-generated or heavily edited images affect Image Authenticity and face-search reliability?
AI-generated or heavily edited faces can produce false confidence: the image may look like a real person, yet no real person exists (synthetic face), or the face may be a swap using a real person’s likeness. These scenarios can yield confusing match sets—some results may relate to the donor face, some to the target face, and some to look-alikes—so you should corroborate with independent evidence (consistent usernames, original sources, additional photos, and non-image signals) rather than relying on a single matched picture.
How can FaceCheck.ID add value when you’re evaluating Image Authenticity in face-search results?
Tools like FaceCheck.ID can help you quickly surface where a face appears across many sites, which is useful for authenticity work: you can look for the earliest/most credible occurrence, spot repeated reuse across unrelated contexts (a common scam indicator), and compare multiple independent instances of the face. However, the same caution applies: even strong matches should be treated as investigative leads, and you should verify the original source and context before drawing conclusions about identity or real-world events.

Recommended Posts Related to image authenticity
-
Reverse Image Search FAQ: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
Verifying image authenticity. Journalists fact-checking image authenticity.
-
Can you reverse image search a person?
All-in-One Tool: Verify profiles, reconnect, and ensure image authenticity.

