Reverse Image Lookup: How to Find Sources Fast
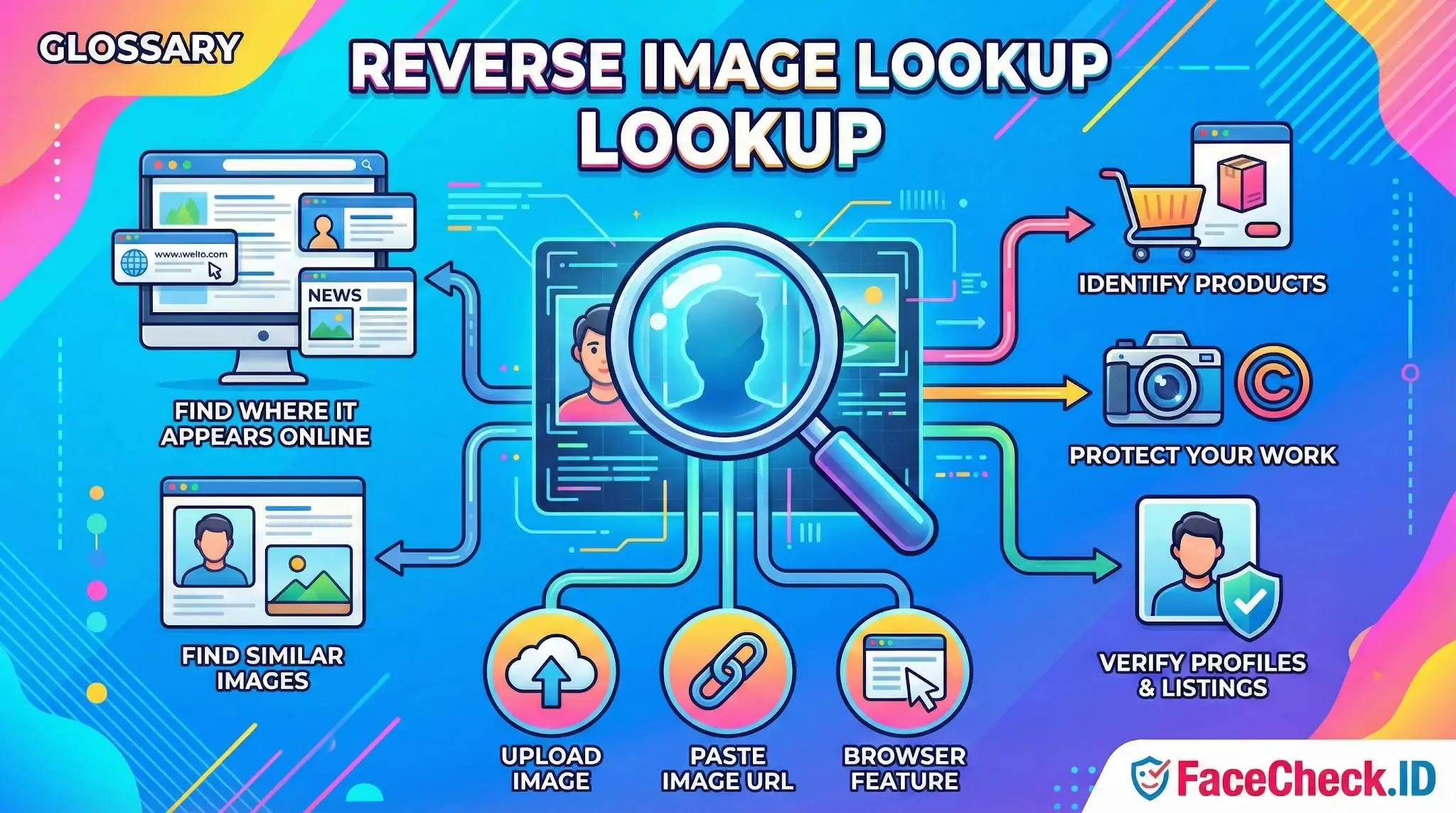
Reverse image lookup is a way to search the internet using a picture instead of typing keywords. You upload an image, paste an image URL, or use a browser feature to find where that image appears online, visually similar images, and related information about what is shown in the picture.
What reverse image lookup does
Reverse image lookup compares the visual content of an image such as shapes, colors, patterns, and objects against images indexed on the web. Results often include:
- Web pages where the same image is published
- Larger or higher quality versions of the image
- Similar images that look alike but are not identical
- Possible matches to a product, person, place, logo, or artwork
- Basic context pulled from matching pages
Common uses
Find the source of an image
Track down the original publisher, photographer, or earliest known upload to understand where an image came from.
Check if an image is real or reused
See if a viral photo has appeared before, is taken out of context, or is linked to misleading stories.
Identify products
Match an item in a photo such as clothing, furniture, gadgets, or decor and find shopping pages or product names.
Protect your work
Creators use reverse image lookup to find copies of their photos, graphics, or designs used without permission.
Verify profiles and listings
Spot stolen profile pictures, fake accounts, and suspicious marketplace listings by checking where else the image appears.
How to do a reverse image lookup
- Upload a file from your device to an image search tool
- Paste an image link to search from a URL
- Use a browser option like right click search image in supported browsers
- On mobile, use a built in image search in some apps or share the image to an image search tool
For best results, use a clear image, avoid heavy crops, and try more than one tool if the first results are limited.
Tips to get better results
- Search with the full image first, then try cropped versions focusing on the main subject
- Use a higher resolution image when possible
- If text is important, try searching both the image and any keywords you already know
- If results look wrong, try a different angle or a screenshot from another frame
Reverse image lookup vs image recognition
- Reverse image lookup focuses on finding where an image appears and what visually similar images exist online.
- Image recognition focuses on identifying what the image contains, such as objects, scenes, and text, even if no exact match exists on the web.
In practice, many tools combine both.
Limitations
Reverse image lookup is not perfect. Results depend on what has been indexed publicly, and some images may not appear due to:
- New uploads not yet indexed
- Private or restricted platforms
- Heavy edits, filters, or overlays
- Very common visuals that generate many similar matches
FAQ
What does “Reverse Image Lookup” mean when the image contains a person’s face?
Reverse Image Lookup usually means searching the web using an image as the query to find exact or near-duplicate copies (same photo, resized, cropped, recompressed, or slightly edited). When the image contains a face, traditional reverse image lookup is still often “image-level” matching, while face recognition search engines can also attempt “person-level” matching (the same individual across different photos).
Why can a reverse image lookup miss the same person even when their face is widely online?
Reverse image lookup can miss the person because it may rely heavily on visual similarity of the entire image (background, clothing, composition) or on duplicate-detection techniques, not on facial features alone. If the person appears in different photos (different lighting, angle, hair, makeup, age, or background), the images may not be “similar enough” at the whole-image level to link them, even though a face-focused engine might.
What is a practical workflow to do a reverse image lookup for faces while reducing wrong-person results?
Start by running a traditional reverse image lookup on the original image (or a clean crop) to find exact duplicates and reposts. Then run a face-focused search using a tight face crop (centered, sharp, minimal filters) to look for the same person across different photos. Finally, cross-check matches by opening the source pages, comparing multiple facial cues across several images, and looking for consistent context (same username, linked profiles, or repeated unique details). Tools like FaceCheck.ID can add value in the face-focused step when you specifically need “same person across different photos,” but results should be treated as leads, not proof.
How do edits (filters, memes, AI upscales, watermarks) affect reverse image lookup vs face recognition search?
Edits that change the overall look of the image (heavy filters, text overlays, frames, stickers, or meme crops) can break traditional reverse image lookup because the full-image similarity changes. Face recognition search engines may still match if the face remains visible and not overly distorted, but heavy beauty filters, face-swap edits, or synthetic/AI-generated faces can increase false matches. For best results, remove overlays when possible and use the clearest, least-edited frame where the face is front-facing and well-lit.
What privacy steps should I take before doing a reverse image lookup on a face photo?
Avoid uploading images that reveal unnecessary personal data (addresses, IDs, children, license plates, medical info, or private messages visible in the screenshot). Prefer a minimal face crop, and consider masking non-essential background details. Review the service’s retention/terms (whether it stores uploads, logs queries, or shares data), and use the results responsibly—don’t treat a match as identity confirmation without independent verification, and avoid sharing sensitive findings that could enable harassment or doxxing.

Recommended Posts Related to reverse image lookup
-
Reverse Image Search FAQ: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
What Is Reverse Image Lookup? Reverse image lookup refers to the process of using an image as a search query instead of text:. Reverse image lookup is a search technique where you provide an image to a search engine, which then returns information about that image, including:.

