Ai-Generated Image Explained: Definition, Uses & Risks
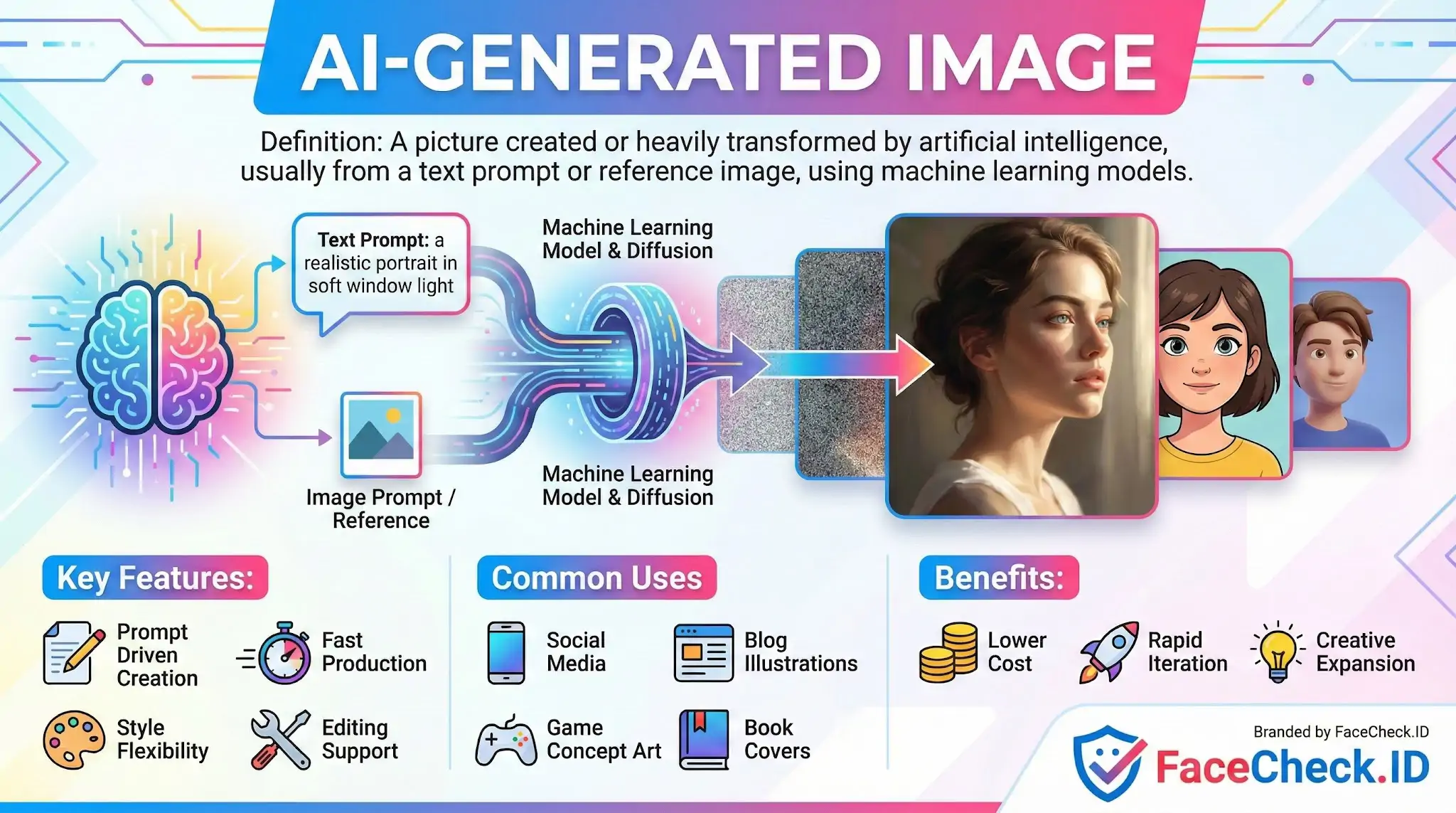
Definition
An AI generated image is a picture created or heavily transformed by artificial intelligence, usually from a text prompt, a reference image, or both. Instead of being drawn or photographed in the traditional way, the image is produced by a machine learning model that predicts what the visual result should look like based on patterns learned from large datasets.
How AI Generated Images Are Created
Most AI image generators use diffusion models or similar techniques. In simple terms, the system starts with visual noise and gradually turns it into a clear image that matches your input.
Common inputs include:
- Text prompt like “a realistic portrait in soft window light”
- Image prompt like a photo used for style transfer or variation
- Settings like aspect ratio, style, seed, and guidance strength
Key Features
- Prompt driven creation: Your words shape the content, style, and details
- Fast production: Images can be generated in seconds to minutes
- High variation: Small prompt changes can create very different results
- Style flexibility: Realistic, cartoon, 3D, watercolor, cinematic, and more
- Editing support: Many tools allow inpainting, outpainting, upscaling, and background changes
Common Uses
AI generated images are widely used for:
- Blog and website illustrations
- Social media graphics and ad creatives
- Product mockups and concept art
- Game and film pre production visuals
- Book covers and album art drafts
- Training data and design experimentation
Benefits
- Lower cost compared to custom illustration or photoshoots
- Rapid iteration for exploring ideas and visual directions
- Accessibility for non designers who need quality visuals
- Creative expansion by generating concepts that are hard to sketch quickly
Limitations and Risks
- Inconsistent details like hands, text, logos, and small objects
- Originality concerns if outputs resemble existing works
- Bias and representation issues based on training data
- Copyright and licensing rules that vary by tool and usage
- Authenticity challenges when images are mistaken for real photos
Best Practices
- Write clear prompts that include subject, style, lighting, camera angle, and mood
- Use negative prompts or constraints to reduce unwanted elements
- Generate multiple variations, then refine with edits
- Avoid using AI generated images for sensitive or high trust contexts without clear labeling
- Check the tool’s license before using images commercially
Related Terms and Clarifications
- AI generated image vs AI edited image: Generated images start from scratch or near scratch, edited images modify existing photos or artwork
- AI generated image vs CGI: CGI is manually modeled and rendered, AI generation is model predicted from prompts and references
- AI generated image vs deepfake: Deepfakes usually target realistic identity swaps or facial reenactment, AI images may be entirely synthetic without a real person
FAQ
What is an AI-generated image in the context of face recognition search engines?
An AI-generated image is a synthetic picture created by a generative model (for example, a diffusion model or GAN) rather than captured by a camera. In face recognition search, an AI-generated face can look realistic but may represent a person who does not exist, or it may blend features from multiple real people—both of which can complicate how search engines interpret “who” the face belongs to.
Can an AI-generated face produce matches to real people in a face search engine?
Yes. Even if a face is fully synthetic, its facial geometry can still resemble real people closely enough that a face search engine may return similar-looking individuals (near matches). This does not prove the synthetic image depicts a real person; it often means the generated face landed near real faces in “face embedding” space, so results should be treated as leads and verified with additional context (source pages, timestamps, consistent identity signals).
How do AI-generated or heavily AI-edited portraits affect face-search reliability and false-match risk?
AI generation and AI “beautification” edits can smooth skin, alter eye shape, change facial proportions, or introduce artifacts that shift a face’s embedding. That can increase false positives (matching the wrong person), reduce true positives (missing the same person), and cause unstable results across searches. The risk is higher when the image is stylized, over-smoothed, low-resolution, or includes exaggerated features common in AI portraits.
What practical checks can help me spot an AI-generated image before relying on face search results?
Use a combination of checks: (1) zoom in for artifacts (asymmetric earrings, strange teeth, messy hair edges, inconsistent eyeglass frames, warped text/logos), (2) look for inconsistent lighting/shadows and unnatural skin texture, (3) review metadata and the upload history on the source page, (4) compare multiple images of the same claimed person for consistent facial details (moles, ear shape, teeth spacing), and (5) run both face search and traditional reverse image search to see whether there is a real-world posting trail. If the image appears only in newly created profiles or repeated across unrelated accounts, treat it as high-risk.
If I upload an AI-generated image to a tool like FaceCheck.ID, how should I interpret the results safely?
Assume results may be “similar face” leads rather than the same person. Prioritize verification steps: open each source page, check whether multiple independent sources consistently connect to the same identity, and confirm with non-face evidence (usernames, cross-posted bios, location consistency, older posts, and corroborating links). If results look scattered across unrelated people, treat the query image as potentially synthetic or heavily edited and avoid concluding that any returned person is the creator, owner, or “real identity” behind the AI-generated face.

Recommended Posts Related to ai-generated image
-
Celebrity Romance Scams 2026: How Scammers Use AI Deepfakes and Stolen Photos to Steal Millions
Warning: Romance scammers are using AI-generated images, deepfakes, and celebrity impersonations to target victims in 2026.
-
How to Spot a Catfish Online in Under 60 Seconds with FaceCheck.ID
FaceCheck.ID is purpose-built for identity verification: advanced facial recognition that handles real-world image variations, combined with integrated AI-generated image detection to flag synthetic faces instantly.
-
How to Spot a Catfish in 2025: Red Flags in Fake Dating Profiles
Detect stolen or AI-generated images.

