Deepfake Detector Explained: How It Flags Fake Media
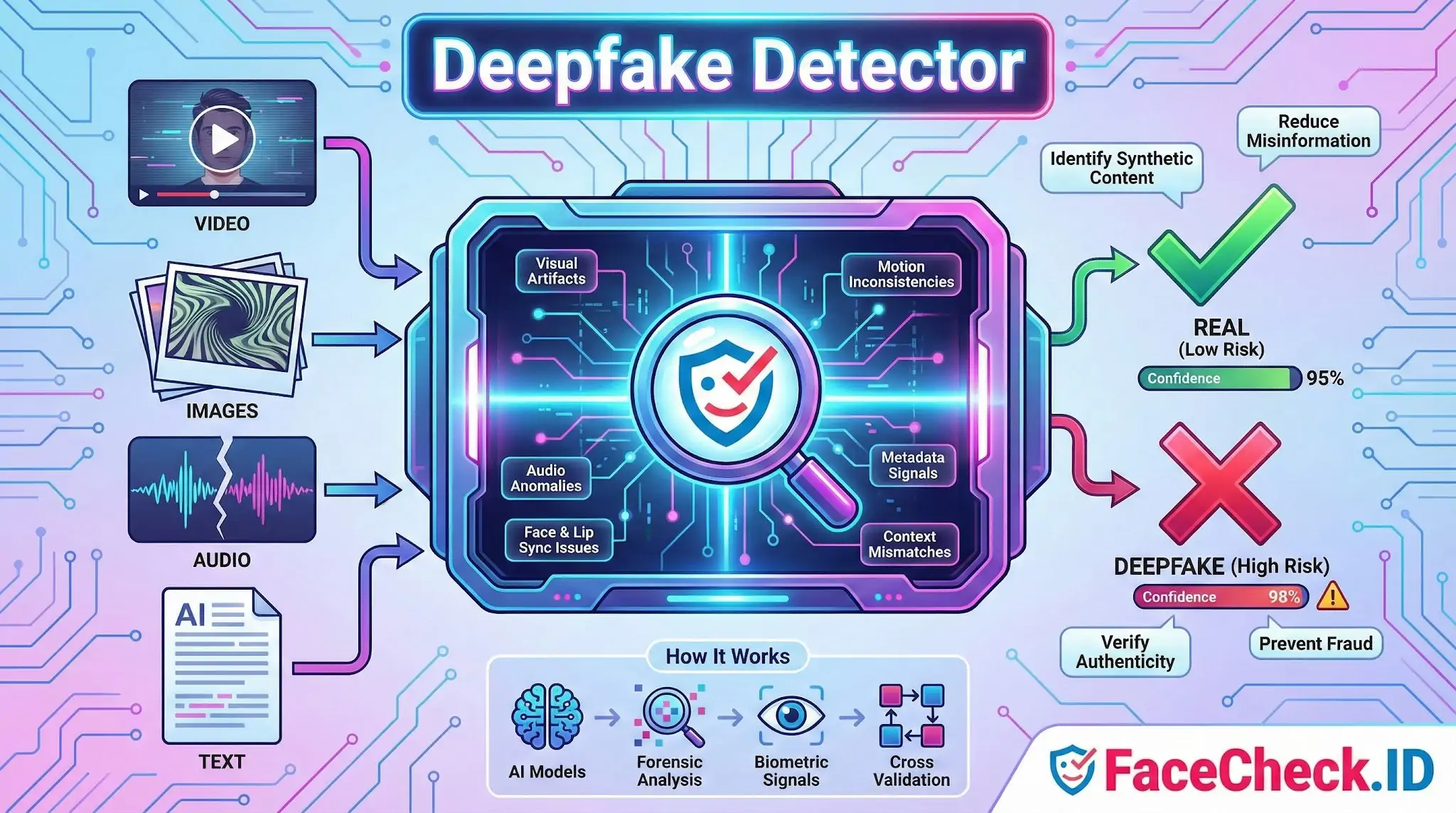
A deepfake detector is a tool or system that helps identify whether a video, image, audio clip, or text has been manipulated using artificial intelligence. Its goal is to spot synthetic or altered content that looks or sounds real, then flag it as potentially fake or high risk.
Deepfake detectors are used by newsrooms, social media teams, businesses, educators, and everyday users to reduce misinformation, prevent fraud, and verify authenticity before sharing or acting on content.
What a deepfake detector checks
Deepfake detectors analyze content for patterns that often appear when AI generates or edits media. Depending on the tool, it may look for:
- Visual artifacts in images and video like unnatural skin texture, inconsistent lighting, odd reflections, warped backgrounds, or mismatched facial features
- Face and lip sync issues such as subtle timing errors between speech and mouth movement
- Motion inconsistencies including unnatural blinking, head movement, or frame to frame glitches
- Audio anomalies like robotic tone, unnatural pauses, missing breath sounds, or frequency patterns common in voice cloning
- Metadata and file signals such as editing traces, compression patterns, and unusual encoding behavior
- Context mismatches where content details conflict with known facts, locations, or timelines
How deepfake detection works
Most modern deepfake detectors use machine learning models trained on large datasets of real and synthetic media. Common approaches include:
- Classifier models that score the likelihood content is AI generated
- Forensic analysis that inspects pixels, frequency domains, and compression footprints
- Biometric and behavior signals like eye movement patterns, facial micro expressions, and speech characteristics
- Cross validation that compares media against trusted sources or checks if a face or voice matches known samples
Many tools output a confidence score or a label such as real, suspicious, or manipulated.
Types of deepfake detectors
Deepfake detection tools usually focus on one or more formats:
- Video deepfake detectors for face swaps and AI altered footage
- Image deepfake detectors for AI generated portraits and edited photos
- Audio deepfake detectors for voice cloning and synthetic speech
- Text detectors for AI generated writing and impersonation attempts
- Multi modal detectors that analyze video plus audio plus context together
Common use cases
A deepfake detector can help with:
- Misinformation checks before sharing viral clips
- Brand and executive impersonation prevention in social engineering attacks
- Fraud detection for KYC, onboarding, and identity verification
- Content moderation on platforms that host user generated media
- Journalism and fact checking when verifying sources and footage
- Digital forensics and incident response investigations
Deepfake detector accuracy and limitations
Deepfake detection is helpful, but not perfect. Results depend on the model, the quality of input, and how new the manipulation method is.
Key limitations include:
- False positives where real content is flagged as fake
- False negatives where high quality deepfakes pass as real
- Quality sensitivity since low resolution, heavy compression, and screen recordings can reduce accuracy
- Arms race effects because deepfake generation techniques evolve quickly
- Context gaps since detectors may not understand real world events or intent
For high stakes decisions, use a detector as one layer of verification rather than the only proof.
How to choose a deepfake detector
When comparing tools, look for:
- Supported formats: video, image, audio, text
- Output clarity: confidence score, explanation, and evidence highlights
- Speed and scale: single file checks vs bulk workflows
- Privacy and security: where files are processed and stored
- Update cadence: how often detection models are refreshed
- Integration options: API access, browser extensions, or platform plugins
Best practices for verifying suspicious media
A deepfake detector works best alongside basic verification steps:
- Check the original source and upload history
- Look for higher quality versions of the same clip
- Compare with trusted reporting and official statements
- Inspect frames, audio continuity, and lighting consistency
- Preserve the original file when possible instead of re shared copies
FAQ
What is a Deepfake Detector in the context of face recognition search engines?
A Deepfake Detector is a set of techniques or tools used to assess whether a face image (or a video frame) may have been AI-generated, face-swapped, or heavily manipulated. In face recognition search engines, it’s used as a safety layer to flag inputs or results that could trigger misleading matches, such as linking a synthetic face to real people or connecting a real person to synthetic content.
Why is deepfake detection useful before running a face recognition search?
If the image is synthetic or face-swapped, a face search may return convincing-but-wrong “same person” hits, because the embedding can resemble multiple real identities. Detecting deepfake indicators first helps you treat matches as lower-confidence leads, avoid false accusations, and decide whether to search using a different (more reliable) photo.
What kinds of deepfake or manipulation issues can distort face-search results?
Common distortions include face swaps, AI “beauty” edits, GAN/ diffusion-generated faces, heavy filters, aggressive retouching, and frames from low-quality or compressed videos. These can change skin texture, eye/teeth details, facial proportions, or add artifacts—sometimes making different people look more alike to the model and increasing wrong-person matches.
If I suspect a photo is a deepfake, what should I upload to a face recognition search engine instead?
Use a clean, high-resolution, front-facing photo from a credible source when possible (e.g., an original profile photo rather than a repost, meme, or screenshot). If your only source is a video, extract multiple frames (neutral expression, good lighting, minimal motion blur) and compare whether the search results are consistent across frames—deepfake-driven frames often produce unstable or contradictory hit patterns.
How should I use FaceCheck.ID results when deepfakes are a possibility?
Treat FaceCheck.ID (or any face search engine) results as investigative leads, not proof of identity, especially if the input could be manipulated. Cross-check top hits by opening the source pages, looking for independent corroboration (same person across multiple unrelated sites, consistent context, timestamps), and verifying non-face cues (tattoos, scars, clothing, event/location context). If results cluster around unrelated identities or switch dramatically when you change frames/photos, that’s a warning sign to suspect synthetic or altered media.

Recommended Posts Related to deepfake detector
-
How to Spot a Catfish in 2025: Red Flags in Fake Dating Profiles
AI deepfake detection: AI-powered tools can now scan profile images and video calls to detect manipulation. The future of safe online dating may rely on crowd reporting + blockchain verification + AI deepfake detection working together.
-
Yilong Ma: Elon Musk's Doppelgänger or a Deepfake Masterpiece?
Deepware's scanner uses advanced AI models to detect signs of digital manipulation in videos, making it a reliable source for deepfake detection. While Deepware's AI models are sophisticated, no deepfake detection system is infallible.
-
How to Spot a Catfish Online in Under 60 Seconds with FaceCheck.ID
AI/Deepfake Detection. How accurate is the AI/deepfake detection?
-
Find & Remove Deepfake Porn of Yourself: Updated 2025 Guide
Stay informed on new protections: laws and tech are evolving, so follow news about deepfake detection, watermarking, and new regulations; organizations listed above often announce new initiatives.

