Bing Visual Search Explained: Search the Web by Image
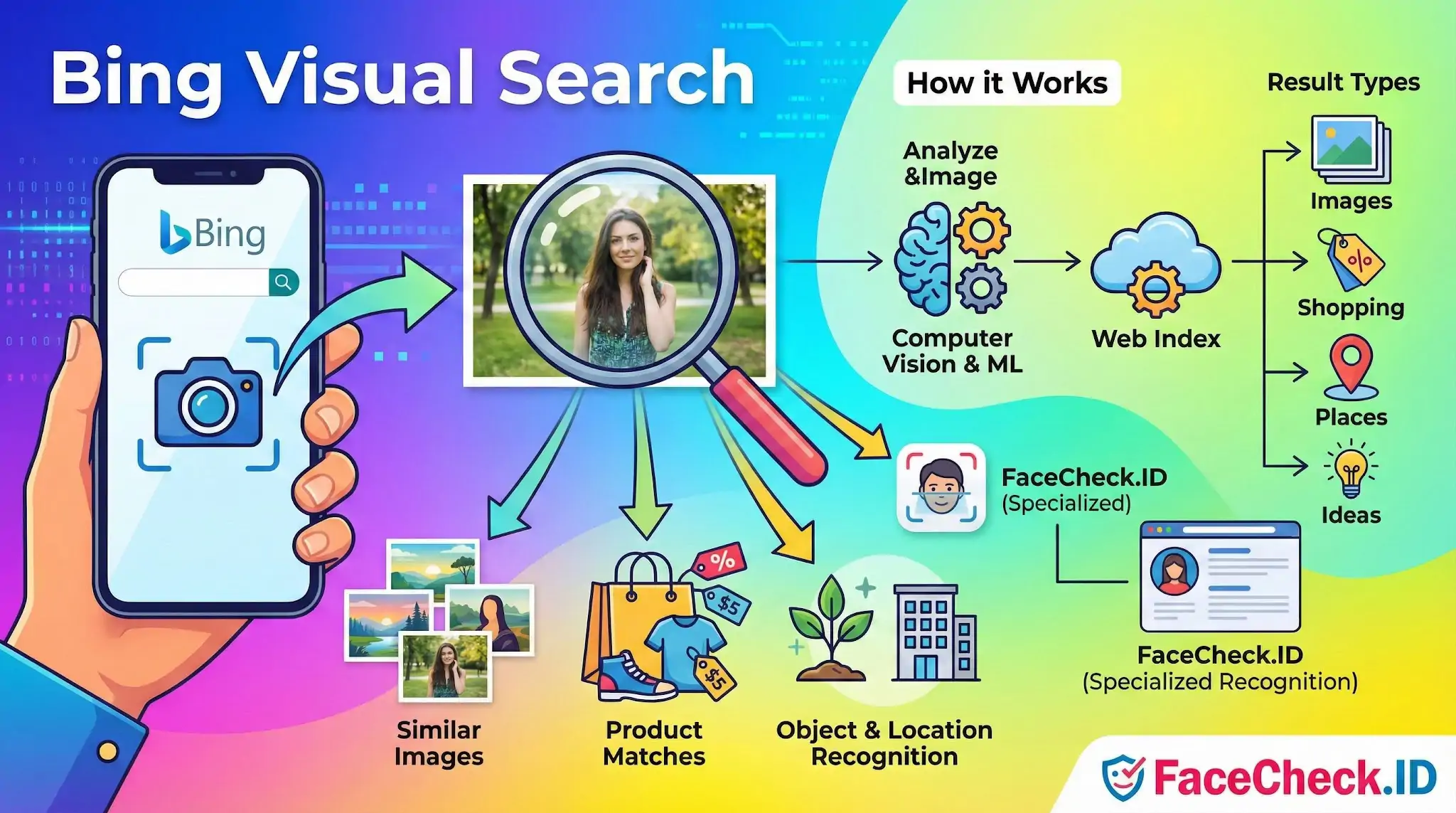
Bing Visual Search is a Microsoft Bing feature that lets you search the web using an image instead of typing keywords. You can upload a photo, paste an image URL, or take a picture on a supported device, and Bing returns visually similar images plus related information such as product matches, places, animals, plants, and objects.
What Bing Visual Search does
- Finds similar images and visually related content
- Identifies objects inside a photo and suggests related topics
- Matches products in an image to shopping results when available
- Recognizes landmarks and locations and links to relevant pages
- Helps discover ideas like outfits, home decor, recipes, and art references
How it works
Bing Visual Search uses computer vision and machine learning to analyze what is shown in an image. It detects key elements like shapes, colors, textures, and objects, then compares them with indexed images and web pages to produce results that closely match what you uploaded.
How to use Bing Visual Search
- Open Bing in a browser.
- Select the visual search icon in the search bar.
- Upload an image, drag and drop a file, paste an image link, or take a photo.
- Review matches, related results, and suggested refinements.
Common uses
- Shopping and price comparison by photographing a product or outfit
- Identifying plants, animals, and objects from a picture
- Finding the source of an image or higher resolution versions
- Exploring similar designs for fashion, interior design, logos, and artwork
- Travel planning by identifying landmarks and attractions
Bing Visual Search vs. traditional search
Traditional search starts with words and returns results based on text relevance. Bing Visual Search starts with an image and returns results based on visual similarity, then adds context such as names, categories, and related web pages.
Tips for better results
- Use clear, well lit images with the main subject in focus.
- Crop the photo to remove distracting background elements.
- Try multiple angles if the object is hard to recognize.
- If results are too broad, use a more specific image or tighter crop.
FAQ
What is Bing Visual Search, and is it a true face recognition search engine?
Bing Visual Search is Microsoft’s tool for searching the web using an image (or a region within an image) to find visually related results. It can surface the same image, close variants, or visually similar content, but it is not typically positioned as a dedicated open-web face-recognition engine that reliably finds the same person across many different photos. For identity-sensitive face lookups, specialized tools (e.g., FaceCheck.ID) may be more purpose-built, but results should still be treated as leads—not proof.
How do I use Bing Visual Search to look up a face photo without uploading unnecessary personal data?
Use a tightly cropped image focused on the face (avoid including bystanders, addresses, license plates, or other sensitive background details). If you only have a screenshot, crop out UI elements and usernames. Prefer using a neutral, front-facing image with good lighting. When possible, search with the minimum-resolution image that still shows key facial features, and avoid re-uploading multiple private photos unless it’s necessary for verification.
Why might Bing Visual Search miss the same person even if their photos are online?
Bing Visual Search often performs best at matching the same image or visually similar images, and it may struggle when the same person appears in different poses, ages, lighting conditions, edits/filters, or across unrelated photos that aren’t visually similar. It can also miss content that isn’t indexed, is blocked from crawling, is behind logins/paywalls, or has been removed/changed since indexing.
What should I check in Bing Visual Search results before assuming a face match is the same person?
Validate using non-face clues across multiple independent sources: consistent biographical details, consistent usernames/handles, cross-linked profiles, matching timestamps/locations, and multiple distinct photos that align (not just one look-alike image). Be cautious with single-source hits, repost sites, or low-quality thumbnails. If the query relates to safety, fraud, or accusations, treat results as preliminary leads and seek corroboration.
When is it better to use a dedicated face search tool like FaceCheck.ID instead of Bing Visual Search?
If your goal is to find the same person across different photos (not just the same image), a dedicated face-search tool (such as FaceCheck.ID) may be more effective because it is designed around facial similarity rather than whole-image similarity. Even then, you should use it carefully: expect false positives, verify matches using multiple independent signals, and avoid using results to harass, doxx, or make high-stakes decisions without additional confirmation.

Recommended Posts Related to bing visual search
-
Reverse Image Search FAQ: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
Bing Visual Search: Free with standard usage. Bing Visual Search (good for products). General-purpose (Google Images, [Bing Visual Search](https://www.bing.com/images/discover), [Yandex](https://yandex.com/images/)).
-
Top 6 Reverse Image Search Mobile Sites to Find People, Products, and Places
Bing Visual Search:. How to Use: Open Bing visual search on your mobile browser. Tips: Bing Visual Search is not just limited to image matches; it can also provide information on similar items, making it great for shopping.
-
How to Reverse Image Search a Screenshot with FaceCheck.ID
Try Bing Visual Search, TinEye, or Yandex.Images for additional results.
-
How to Use Reverse Image Search to Find LinkedIn Profiles by a Photo
In such cases, it may be helpful to try other reverse image search engines like Google Images, Bing Visual Search, or TinEye.
-
How to Find Images on the Web
-
Should I reverse image search myself?
Bing Visual Search: Microsoft's Bing also offers a visual search feature.

