Identity Theft Explained: Types, Risks & Prevention
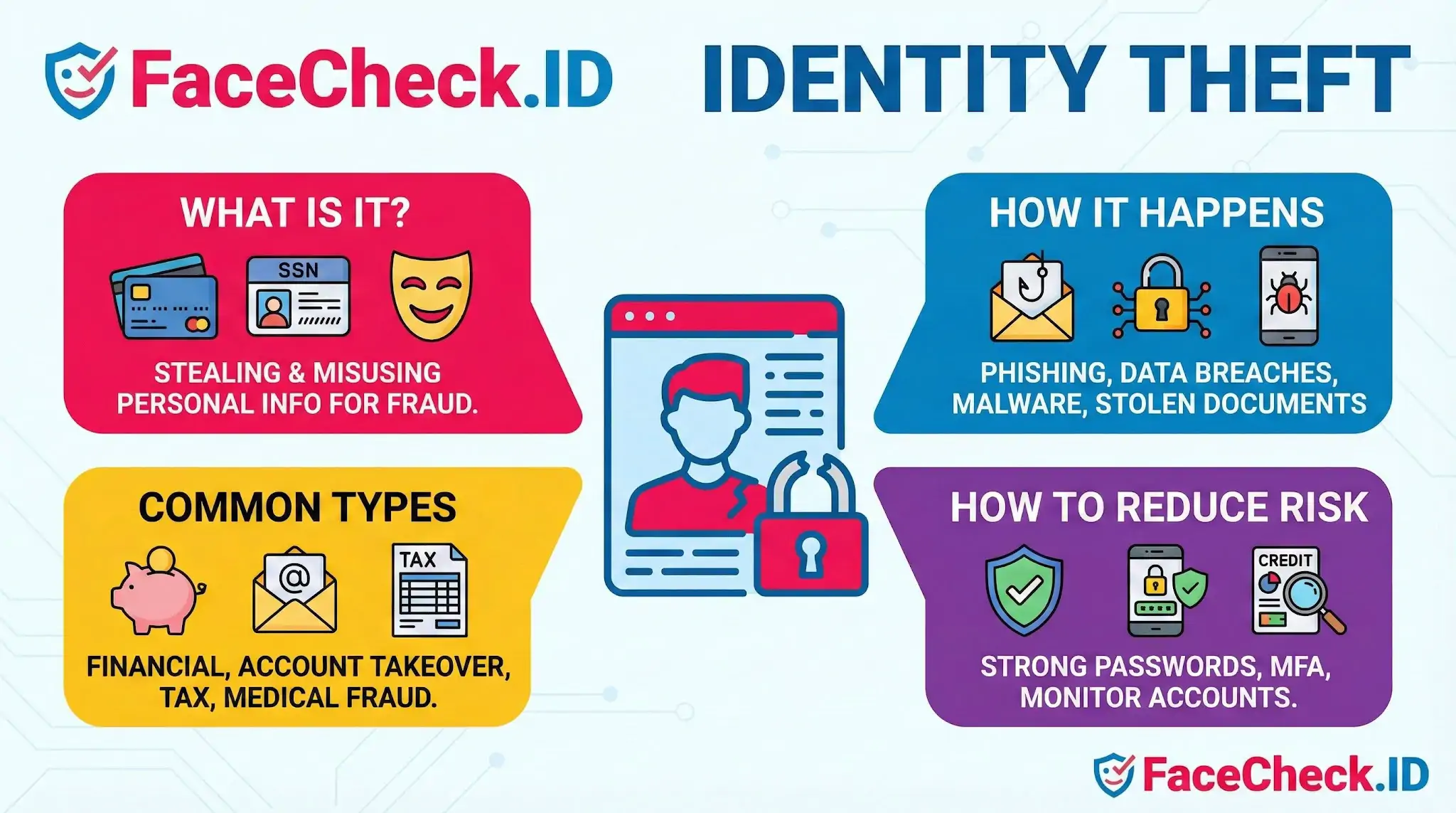
Identity theft is when someone steals your personal information and uses it to pretend to be you, usually to get money, credit, services, or other benefits.
What counts as identity theft?
Identity theft can involve stealing or misusing details such as:
- Full name and date of birth
- Social Security number (SSN)
- Driver’s license or state ID number
- Bank account and routing numbers
- Credit or debit card numbers
- Online login details (email, banking, shopping, social media)
- Taxpayer information used to file a fake return
Common types of identity theft
Identity theft can take several forms, including:
- Financial identity theft: opening credit cards or loans in your name, draining accounts, or making unauthorized purchases
- Account takeover: breaking into existing accounts like email, banking, or social media and changing passwords or settings
- Tax identity theft: filing a tax return using your SSN to claim a refund
- Medical identity theft: using your identity to get medical care or prescriptions
- Employment identity theft: using your information to get a job or pass background checks
How identity theft happens
Criminals often get personal data through:
- Phishing emails and fake websites
- Data breaches that expose customer records
- Malware or spyware on computers and phones
- Stolen wallets, mail theft, or document theft
- Weak or reused passwords
Why identity theft is serious
Using your identity can lead to:
- Fraudulent charges and drained accounts
- New debts and damaged credit
- Account lockouts and lost access to services
- Time consuming cleanup with banks, creditors, and agencies
How to reduce your risk
Practical steps that help:
- Use strong, unique passwords and a password manager
- Turn on multi factor authentication (MFA) for key accounts
- Watch bank and credit card statements for unfamiliar activity
- Check your credit reports regularly
- Be careful with links, attachments, and requests for personal details
Quick definition (for glossary)
Identity theft is the theft and misuse of someone’s personal identifying information to impersonate them and commit fraud or other crimes.
FAQ
How can face recognition search engines be used to detect identity theft or impersonation?
They can help you spot where a face photo is being reused across the public web (e.g., the same face appearing on multiple profiles or listings). That pattern can indicate impersonation, stolen photos, or synthetic profile activity. Treat results as leads: confirm by checking the source page context, timestamps, and whether the account shows consistent personal history.
What are common signs in face-search results that suggest someone stole a person’s photos for identity theft?
Common warning signs include: the same face tied to multiple unrelated names/usernames, the same headshot used across different platforms with conflicting biographies/locations, the photo showing up on scam-report or repost/scrape sites, and sudden clusters of near-identical profiles. Any single sign can be benign, but multiple inconsistencies raise risk.
If I find my face photo in face-search results on accounts I don’t control, what should I do to reduce identity-theft risk?
Collect evidence first (URLs, screenshots, dates), then report the impersonating accounts to each platform and request takedown. If available, use the search engine’s removal/opt-out process for the result pages. Strengthen your own accounts (unique passwords, MFA), monitor for new accounts or financial/credential misuse, and consider placing fraud alerts or credit monitoring if personal data is involved.
What are the biggest privacy and security risks of uploading a face photo to investigate identity theft, and how can I reduce them?
Risks include exposing a sensitive face image to a third party, potential retention of uploads, and linking the upload to your IP/device/browser identifiers. To reduce risk: use the minimum necessary image (crop to face, remove backgrounds), avoid including bystanders, use a fresh screenshot without metadata when possible, review the tool’s retention/removal policy, and consider using a separate browser profile or privacy protections while keeping your activity lawful.
How can FaceCheck.ID (or similar tools) help in an identity-theft investigation without over-identifying someone?
Tools such as FaceCheck.ID can help quickly surface public-web pages where a face appears, which can be useful for finding impersonating profiles or reused photos. To avoid over-identification: corroborate with multiple independent signals (same unique photos, consistent usernames, mutual links, long-lived accounts), prioritize original sources over reposts, and never treat a face match alone as proof of a person’s real-world identity.

Recommended Posts Related to identity theft
-
How to Reverse Image Search Mugshots
Preventing identity theft: By verifying the identities of individuals in various online and offline contexts, FaceCheck.ID could contribute to reducing instances of identity theft and fraud.
-
How to Spot a Catfish Online in Under 60 Seconds with FaceCheck.ID
Identity Theft Resource. Consider Identity Theft Protection.
-
How to Find Someone with a Photo?
You can use Social Catfish to verify people, find identity thefts, ensure the credibility of dating ads, reconnect with relatives or friends, and find copyright violations of your photographs.

