Identity Verification Explained: Steps, Types & Uses
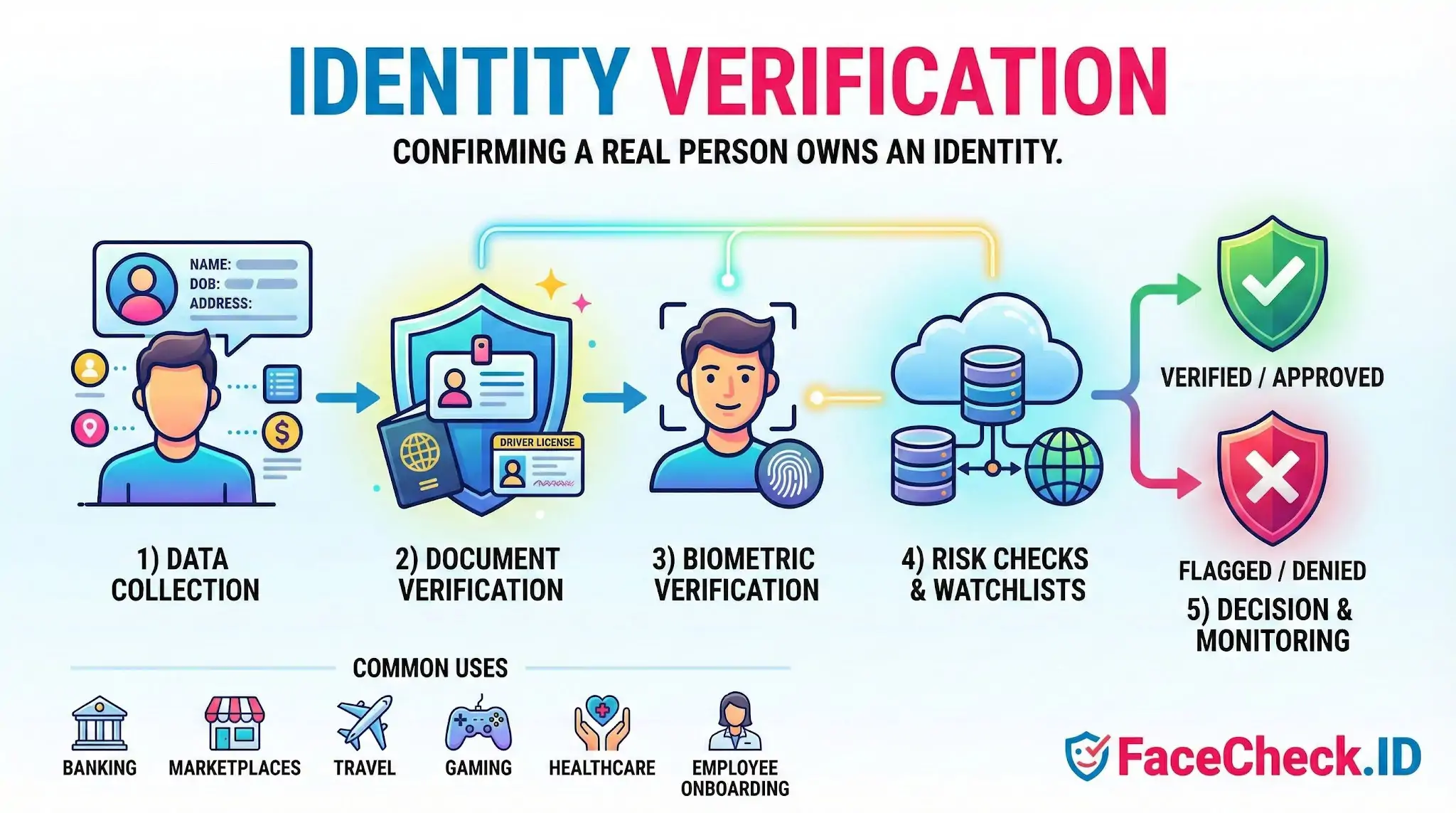
Identity verification is the process of confirming that a person is real and is the legitimate owner of an identity. Businesses use identity verification to reduce fraud, meet legal requirements, and ensure only authorized users can access accounts, make payments, or complete sensitive actions.
Why identity verification matters
- Prevents fraud and account takeover by stopping criminals from using stolen or synthetic identities
- Supports compliance with rules such as KYC and AML in regulated industries
- Builds trust and safety in marketplaces, fintech apps, and online communities
- Reduces chargebacks and financial losses by validating users before transactions
How identity verification works
Most identity verification flows combine several checks to confirm identity with high confidence.
1) Identity data collection
A user provides basic information such as name, date of birth, address, and sometimes a government ID number. Systems may also validate formatting and consistency.
2) Document verification
A user submits images of a government issued ID, such as:
- Passport
- Driver’s license
- National ID card
Software checks security features, document validity, expiration dates, and signs of tampering. Optical character recognition extracts data to compare against the user’s inputs.
3) Biometric verification
Biometrics verify that the person presenting the ID is the same person using the service. Common methods include:
- Selfie match: compares a live selfie to the ID photo
- Liveness detection: confirms the user is present, not a photo, video, or deepfake
- Face recognition: measures similarity between face images within a threshold
4) Database and risk checks
Depending on the use case, systems may cross check against:
- Watchlists and sanctions lists
- Phone and email reputation signals
- Address verification and identity history
- Device fingerprinting and IP geolocation
- Fraud patterns and velocity checks
5) Decision and ongoing monitoring
The system either approves, denies, or flags a user for manual review. For higher risk activities, businesses may use continuous or periodic re verification and step up checks during suspicious events.
Common types of identity verification
- Online identity verification: remote checks via web or mobile, often using ID plus selfie
- In person identity verification: performed at a branch or point of service
- Knowledge based verification: questions based on personal history, now less trusted due to data breaches
- Two factor and multi factor authentication: verifies account access, not identity alone, but often used alongside ID verification
- Age verification: confirms a user meets a required age, sometimes using an ID scan or attribute based checks
Where identity verification is used
- Banking, lending, and crypto onboarding
- Payments and money transfers
- Marketplaces and gig platforms
- Travel, hospitality, and car rentals
- Healthcare portals and telemedicine
- Online gaming, social networks, and dating apps
- Employee and contractor onboarding
Identity verification vs authentication
- Identity verification confirms who a person is, typically during onboarding or major account changes.
- Authentication confirms that the same user is returning, often through passwords, passkeys, OTP codes, or biometrics on a device.
Key terms you may see
- KYC (Know Your Customer): customer identity checks required in many financial services
- AML (Anti Money Laundering): policies and screening to prevent illicit funds
- CIP (Customer Identification Program): US requirements for verifying customer identity
- PEP screening: checks for politically exposed persons
- Sanctions screening: checks against restricted party lists
- Synthetic identity fraud: fake identity built from real and fabricated data
Best practices for effective identity verification
- Keep the flow fast on mobile with clear instructions and good image capture
- Use layered checks and risk based step up verification to reduce user friction
- Combine document, biometric, and device signals for stronger protection
- Provide a manual review path for edge cases and accessibility needs
- Store and process data securely, using encryption and strict retention policies
- Monitor verification performance to balance approval rates and fraud prevention
FAQ
What does “Identity Verification” mean when using a face recognition search engine?
In face-recognition search, “Identity Verification” usually means checking whether a person’s claimed identity (name/account/profile) is consistent with evidence found online for the same face. It’s a confidence-building step (a lead), not a guaranteed proof of identity, because open-web results can be incomplete, outdated, or misattributed.
Why isn’t a face recognition search engine enough for true identity verification?
Face search typically lacks controls that formal identity verification requires—such as document authenticity checks, liveness detection, chain-of-custody, and verified enrollment. Even a strong match can be a look-alike, a reused photo, or an edited/AI-generated image, so face search should support verification workflows rather than replace them.
How can face recognition search results be used responsibly in an identity verification workflow?
Use results to corroborate or challenge a claim: compare multiple photos of the claimed person, look for consistent cross-site signals (same username, biography, locations, timestamps), and validate the original source page rather than relying on reposts. Treat mismatches or mixed results as a prompt for additional verification steps—not as evidence of wrongdoing.
What are common red flags in face-search results that suggest identity verification risk?
Frequent red flags include: the same face tied to multiple unrelated names or profiles; many low-quality repost pages with no clear original; heavy filtering/beauty edits across images; results that cluster around different ages/ethnicities/face shapes; and a “too perfect” portfolio-like trail that appears manufactured. Any of these can indicate photo reuse, impersonation, or synthetic/edited media.
How does FaceCheck.ID add value to identity verification checks without “confirming” identity?
Tools like FaceCheck.ID can help surface where a face appears on the public web, which can support identity verification by finding additional context (other photos, repost patterns, or conflicting identities). The safest approach is to use FaceCheck.ID results to gather leads and then verify through independent steps (direct communication, platform verification, official IDV processes), rather than treating a match list as confirmation.

Recommended Posts Related to identity verification
-
Reverse Image Search - Social Catfish vs FaceCheck.ID
Enter the world of reverse lookup and identity verification services like Social Catfish and FaceCheck.ID! Whether you're playing detective on a potential date or just satisfying your curiosity, these identity verification tools have got your back. Whatever information you have, Social Catfish can help you uncover the mystery, making it one of the best tools for identity verification online.
-
Examining the State-of-the-Art in Facial Recognition Algorithms for Unconstrained Environments
The ability to accurately identify individuals from facial images has important applications in various domains, including access control, surveillance, identity verification, and forensic investigations. The algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard benchmarks such as LFW and is used for various applications such as access control and identity verification. The algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard benchmarks such as LFW and is used for various applications such as access control and identity verification.
-
How to Spot a Catfish Online in Under 60 Seconds with FaceCheck.ID
FaceCheck.ID is purpose-built for identity verification: advanced facial recognition that handles real-world image variations, combined with integrated AI-generated image detection to flag synthetic faces instantly. Pro Tips for More Accurate Identity Verification.
-
How to Detect Fake Remote IT Workers with Facial Recognition (2026 Guide)
Identity verification is now a cybersecurity requirement, not an HR formality. FaceCheck.ID gives hiring teams identity-verification capabilities once available only to government agencies and elite security teams. These takeaways support the need for stronger identity-verification processes, especially for companies hiring remote technical talent.
-
Top 5 Reverse Image Search APIs for Your Projects
Integrate it with security systems and identity verification platforms.
-
Unmasking Romance Scams: Expert Tips to Identify and Avoid Falling Victim
Identity verification - Upload photos of an online match to check against known scammer images and databases.
-
Elder Fraud Statistics 2025: FTC Reports $2.4 Billion Lost to Scams Targeting Seniors
SocialCatfish — identity verification & people search.
-
Can You Reverse Image Search a Face?
Facial recognition technology, while offering benefits like identity verification, poses significant ethical and privacy concerns.
-
Yilong Ma: Elon Musk's Doppelgänger or a Deepfake Masterpiece?
It also underscores the challenges in using facial recognition as a definitive tool for identity verification, as it could potentially be fooled by lookalikes.
-
Reverse Image Search FAQ: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
Identity verification for financial services.

