Computer Vision Explained: How It Works & Uses
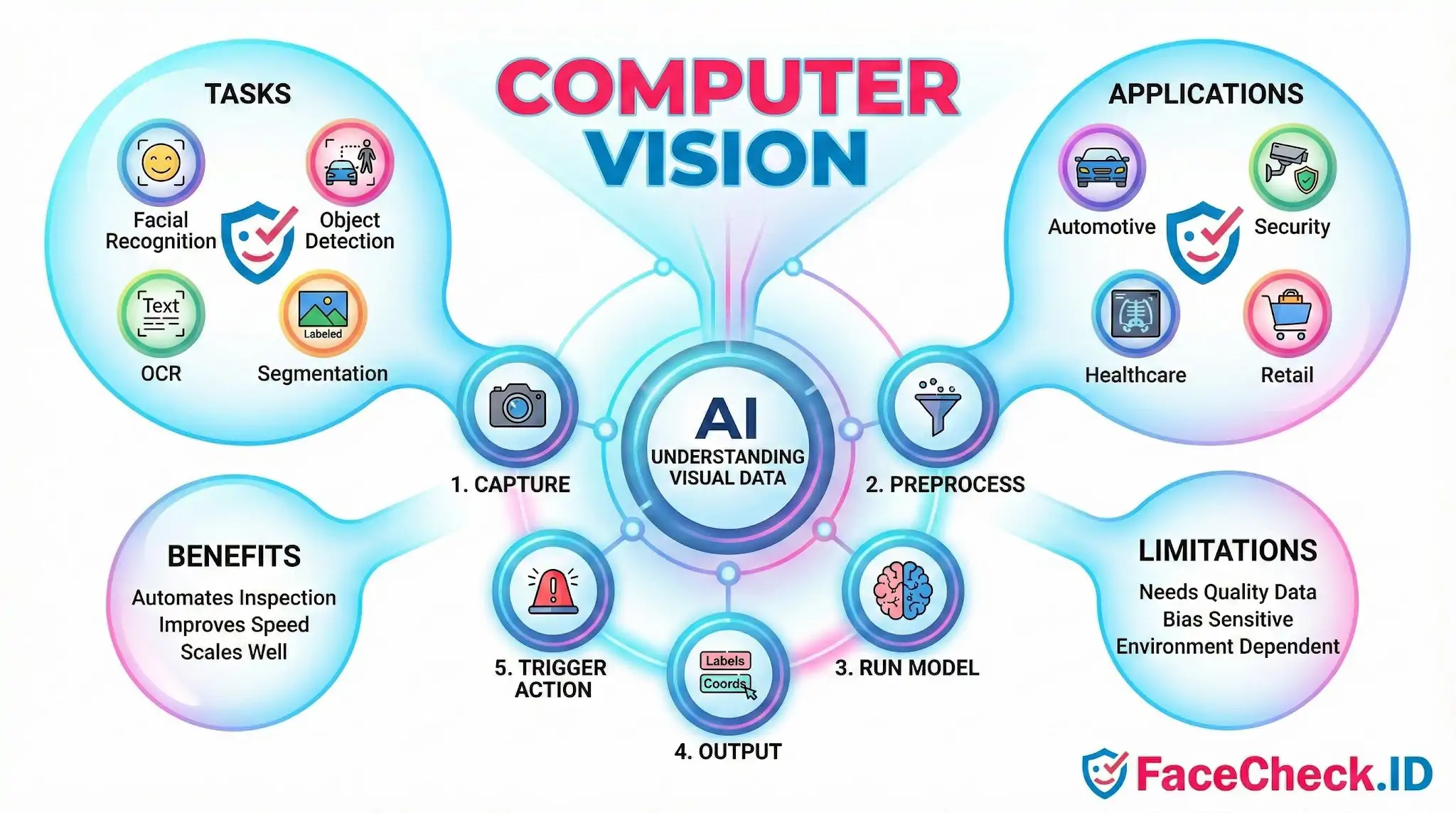
Definition
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that helps computers understand images and video. It uses data from cameras, photos, and video streams to recognize what is in a scene and what is happening.
How computer vision works
Most computer vision systems follow a simple flow:
- Capture visual data from a camera, image file, or video.
- Preprocess the input (resize, normalize, reduce noise, improve contrast).
- Run a model (often deep learning) to detect patterns and make predictions.
- Output results like labels, coordinates, masks, or tracking IDs.
- Trigger an action such as an alert, a decision, or a recommended next step.
What computer vision can do
Common computer vision tasks include:
- Image classification: Identify what an image contains (for example, dog vs cat).
- Object detection: Find and locate objects in an image (for example, pedestrians, cars).
- Image segmentation: Label pixels to separate objects from the background.
- Optical character recognition (OCR): Read text from images.
- Facial detection and recognition: Find faces and match identities (when appropriate and allowed).
- Pose estimation: Detect body joints and movement.
- Video tracking: Follow objects across frames.
- Anomaly detection: Spot unusual events or defects.
Real world applications
Computer vision is widely used across industries, including:
- Automotive: Driver assistance, lane detection, pedestrian detection, autonomous driving features.
- Security and safety: Access control, threat detection, workplace safety monitoring.
- Healthcare: Medical imaging analysis, diagnostics support, clinical workflow assistance.
- Retail and logistics: Shelf monitoring, inventory checks, package sorting, quality control.
- Manufacturing: Defect detection, measurement, robotic guidance.
- Media and entertainment: Filters, visual effects, content tagging, sports analytics.
Benefits and limitations
Benefits
- Automates visual inspection and decision making
- Improves speed and consistency
- Scales better than manual review for large image and video datasets
Limitations
- Needs high quality data and good lighting or camera angles
- Can be sensitive to bias in training data
- Performance can drop when conditions change (new environments, camera types, or object styles)
- May require careful privacy, security, and compliance controls
Related concepts
Computer vision overlaps with machine learning, deep learning, image processing, and pattern recognition. In many modern systems, neural networks such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViT) are used to learn visual features directly from data.
FAQ
How do face recognition search engines handle changes in appearance (aging, hair, makeup, glasses)?
Most face recognition search engines rely on a face “embedding” that emphasizes relatively stable facial structure (e.g., distances and proportions) more than transient details. Moderate changes (new hairstyle, glasses, makeup, facial hair, minor aging) often still match, but accuracy can drop with large appearance shifts, heavy edits/filters, extreme lighting, or very low-resolution images. Using a clear, front-facing photo with good lighting and minimal occlusion typically improves results.
Why can two different face recognition search engines give different results for the same photo?
Differences usually come from (1) the underlying face recognition models and how they were trained, (2) the size and types of websites each service has indexed, (3) face detection/cropping and image-quality handling, (4) ranking logic and similarity thresholds, and (5) how duplicates and near-duplicates are clustered. For example, a tool like FaceCheck.ID may surface different matches than another engine if their indexes, thresholds, or result-grouping strategies differ.
How should I interpret multiple matches returned for one face (and avoid jumping to conclusions)?
Treat matches as leads, not proof of identity. Compare multiple photos for consistent, distinctive features (ear shape, facial proportions, scars/moles), check whether the matched pages show consistent context (same name/handles, locations, timelines), and look for independent corroboration across different sources. Be cautious with recycled images, memes, AI-edited photos, and low-quality thumbnails, which can inflate apparent similarity.
What are the most common technical reasons a face search returns no results even if the person is online?
Common reasons include: the person’s images aren’t publicly accessible (private accounts, paywalls, robots.txt blocks), the engine hasn’t indexed the relevant sites yet, the face is too small/blurred/occluded for reliable detection, the query photo is heavily edited or AI-generated, or the person’s online photos differ substantially from the query image (angle, lighting, age). Trying a sharper, higher-resolution crop and a second photo from a different moment can help.
What safeguards should I use when relying on face recognition search results for safety or fraud checks?
Use results responsibly: avoid doxxing or harassment, and never treat a match as definitive identity proof. Cross-check with non-face signals (usernames, bios, timestamps, reverse image search for exact duplicates, and consistent context across multiple pages). If using a service such as FaceCheck.ID, review multiple returned images and sources before taking action, and consider the risk of look-alikes, reposts, and misattribution—especially for high-stakes decisions.

Recommended Posts Related to computer vision
-
Examining the State-of-the-Art in Facial Recognition Algorithms for Unconstrained Environments
Facial recognition is a rapidly developing field of computer vision and artificial intelligence that has attracted considerable attention from both researchers and practitioners in recent years. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp.
-
How to Search Facebook by Photo
Reverse image search engines use a process called "computer vision" to analyze the pixels in an image and identify patterns and shapes.
-
Leveraging Facial Recognition Technology to Combat Human Trafficking
Traffic Jam uses AI techniques like facial recognition, computer vision, and machine learning to analyze online data and save investigators time.
-
How-To Guide for Effective Face Lookup
Trueface: Trueface is a company that uses computer vision technology to turn video and images into useful information.
-
Reverse Image Search FAQ: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
Reverse image search employs sophisticated computer vision and AI techniques:. From a computer: Visit Google Images, [TinEye](https://tineye.com), or [Yandex Images](https://yandex.com/images/). Analyzes visual content using computer vision algorithms.

