Facial Recognition Software Explained: How It Works
Facial recognition software is a technology that identifies or verifies a person by analyzing their face in a photo, video, or live camera feed. It measures and compares unique facial features, then matches them against a database of known faces to confirm identity or find a likely match.
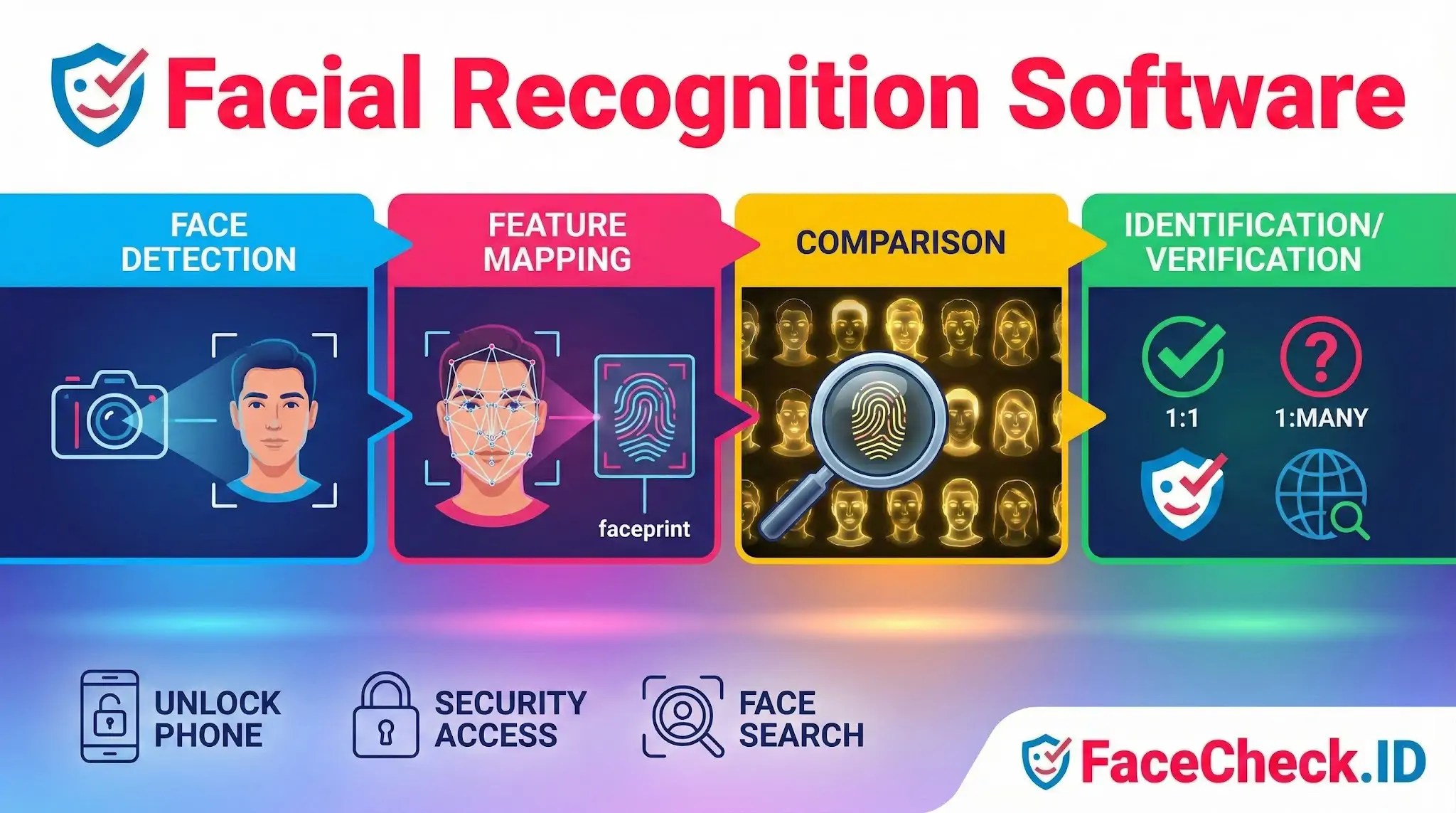
How Facial Recognition Software Works
Most facial recognition systems follow a similar process:
- Face detection
The software finds a human face within an image or video frame.
- Feature mapping
It converts key facial characteristics into a digital template, sometimes called a faceprint.
- Comparison and matching
The template is compared to stored templates in a database to return a match score.
- Identification or verification
- Verification (1:1) checks if a person is who they claim to be.
- Identification (1:many) searches for who the person might be within a database.
Common Uses
Facial recognition software is widely used for:
- Security and access control for buildings, airports, and restricted areas
- Device authentication like unlocking phones or approving logins
- Fraud prevention in banking and online services
- Public safety and surveillance where permitted by law
- Photo organization that groups images by the same person
- Reverse image and face search to locate similar faces across stored image collections or online sources, depending on the platform and tool
Key Benefits
- Fast identity checks and streamlined access control
- Reduced reliance on passwords or physical badges
- Automated monitoring in high traffic environments
Important Considerations
Facial recognition accuracy can be affected by lighting, camera angle, image quality, masks, and changes in appearance. Privacy and legal requirements also vary by location, so organizations often need clear consent policies, strong data security, and compliance with local regulations.
FAQ
What is Facial Recognition Software in the context of a face recognition search engine?
In face recognition search engines, Facial Recognition Software is the technology that detects a face in a photo, converts it into a mathematical representation (often called an embedding or face template), and then compares that representation against an indexed set of other faces to retrieve visually similar matches.
How does Facial Recognition Software decide what to show first in face search results?
Most face search tools rank results by similarity between the uploaded face’s embedding and candidate embeddings in their index. Higher-ranked results usually share more facial-feature geometry in the model’s feature space, but ranking can also be influenced by image quality (sharpness, lighting, pose) and whether the engine groups near-duplicates or multiple sightings from the same source.
What are the biggest limitations of Facial Recognition Software for open-web face search?
Open-web face search is limited by what is actually indexed and accessible (many pages are private, blocked, or not crawled), and by image conditions (low resolution, heavy compression, extreme angles, masks, and occlusions). Even strong models can return look-alikes, outdated images, or unrelated people when the query photo is low quality or when many similar-looking faces exist.
How can Facial Recognition Software be misused, and what safe-usage rules should I follow?
It can be misused for stalking, harassment, doxxing, or making unverified accusations. Safer practice is to treat results as investigative leads, not proof of identity; verify using multiple independent signals (consistent usernames, timestamps, locations, corroborating photos, and context); avoid publishing personal data; and follow applicable privacy laws, site terms, and consent norms—especially when the subject could be a private individual.
If I use a tool like FaceCheck.ID, what does Facial Recognition Software actually do with my photo and results?
In tools such as FaceCheck.ID, the facial recognition component typically extracts a face embedding from your uploaded image and searches the service’s indexed sources for similar embeddings, returning links or source pages where similar faces appear. You should assume uploads and search logs may create privacy risk, so only upload images you have the right to use, minimize sensitive metadata (crop to the face, remove backgrounds when possible), and use any available opt-out/removal channels if your own face appears in results.

Recommended Posts Related to facial recognition software
-
Leveraging Facial Recognition Technology to Combat Human Trafficking
Facial recognition software, such as FaceCheck.ID's facial search engine, plays a critical role in these investigations by analyzing facial features and comparing them with social media profiles, escort workers, and wanted criminals. Facial Recognition Software.
-
Facial Recognition Resources
Amazon Pauses Police Use of Its Facial Recognition Software. The announcement was a striking change for Amazon, a prominent supplier of facial recognition software to law enforcement. The New York Times has developed a tool called Who The Hill that uses facial recognition software to identify members of Congress.
-
Google's Image Search vs. Yandex's Image Search: A Detailed Look
Facial Recognition Software: Use and Databases. Facial recognition software is now widely available.
-
Is There a FREE Facial Recognition Site?
I tried Amazon's controversial facial recognition software. I tried Amazon's controversial facial recognition software.
-
Find YouTubers by Photo using Facial Recognition
The site uses facial recognition software to search for matches.
-
LinkedIn Reverse Image Search to Find LinkedIn Profiles by Photo Using Facial Recognition
You can use facial recognition software to search for LinkedIn profiles by image.
-
Find Twitter Profiles by Photo using Search by Face Engine
The more data the facial recognition software has to work with, and the more accurate the results will be.
-
Should I reverse image search myself?
No, Google's reverse image search doesn't employ facial recognition like specialized facial recognition software does.

